does autoclaving treat rnase|can rnase be inactivated : advice Autoclaving does inactivate DEPC by causing hydrolysis of diethylpyrocarbonate. CO2 and EtOH are released as reaction by-products. DEPC has a half-life of approximately 30 minutes in water, and at a DEPC concentration of 0.1%, solutions autoclaved for 15 minutes/liter can be assumed to be DEPC-free. 3. Find great deals on eBay for Autoclaves. Shop with confidence.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Autoclave low pressure tubing is furnished in random lengths between 20 feet (6 .
Autoclaving glassware and plasticware may not be sufficient to inactivate RNase. Bake glassware for 4 h at 300°C. Treat plasticware either with DEPC or commercially available products that inactivate RNase upon contact (e.g., RNaseZap from Ambion).Autoclaving does inactivate DEPC by causing hydrolysis of diethylpyrocarbonate. CO2 and EtOH are released as reaction by-products. DEPC has a half-life of approximately 30 minutes in water, and at a DEPC concentration of 0.1%, solutions autoclaved for 15 minutes/liter can be assumed to be DEPC-free. 3.
Autoclaving does not protect completely against RNAses, but it still reduces RNAse activity significantly. So while you should not rely on autoclaving to get rid of RNAses, in my experience it is sufficient if you start from a source that is unlikely to contain a lot of RNAses.RNase and DEPC Treatment: Fact or Laboratory Myth . Autoclaving alone does indeed inactivate a substantial amount of RNase A (Figure 1). Various concentrations of RNase A were added to PBS and .
Treat glassware and plasticware with RNase-inactivating agents. Glassware should be baked at +180°C for at least 4 hours. . rinsed with DEPC or DMPC (dimethyl pyrocarbonate) treated water and heated to +100°C for 15 minutes in an autoclave. To treat water with DEPC (or DMPC, dimethyl pyrocarbonate, a less toxic alternative to DEPC that can .Wherever possible, treat solutions with 0.1% DEPC for at least 1 h at 37˚C, and then autoclave for 15 min at 15 psi (1.05 kg/cm2) on liquid cycle. † Autoclaving glassware and plasticware may not be sufficient to inactivate RNase. Bake glassware for 4 h at 300˚C. Treat plasticware either with DEPC or commercially available products that
DNase can be destroyed by autoclaving for 15 minutes at 121°C (250°F) or by following any of the procedures listed below. One or more of the following techniques will inhibit or remove RNase from your plastic container. Match the resin code on the bottom of your Nalgene® container with the correct technique.Figure 2. Effects of DEPC Treatment of Various Buffers. One µg/ml RNase A was added to various buffers along with 0.1% or 1% DEPC. Solutions were vigorously shaken for 1 minute, incubated for 1 hour at room temperature and autoclaved for 25 minutes. 1 µl of each solution was mixed with 1 ng of a 5 x 10 4 cpm 304 nt RNA probe and incubated at 37°C for one hour. 5 µl .
Controlling RNase Contamination Working with RNA can be intimidating. Environmental RNase contamination sources include microbial contamination from room air as well as RNases from human skin, hair, or saliva. RNase inactivation methods range from DEPC treatment followed by autoclaving to more
These current methods of RNase inactivation tend to be costly, time-consuming and wasteful. They include DEPC treatment of water and autoclaving, chemical decontamination of surfaces and chemical treatment of equipment followed by rinsing in RNase-free water and baking glassware. It is difficult to know when a lab is clean enough.Figure 2. Effects of DEPC Treatment of Various Buffers. One µg/ml RNase A was added to various buffers along with 0.1% or 1% DEPC. Solutions were vigorously shaken for 1 minute, incubated for 1 hour at room temperature and autoclaved for 25 minutes. 1 µl of each solution was mixed with 1 ng of a 5 x 10 4 cpm 304 nt RNA probe and incubated at 37°C for one hour. 5 µl .At autoclaving temperature and pressure, DEPC degrades into carbon dioxide and ethanol, both of which are quite volatile under these conditions. Alternative approaches include (1) . (DEPC) is a well-known ribonuclease or RNase inhibitor. It is .Figure 2. Effects of DEPC Treatment of Various Buffers. One µg/ml RNase A was added to various buffers along with 0.1% or 1% DEPC. Solutions were vigorously shaken for 1 minute, incubated for 1 hour at room temperature and autoclaved for 25 minutes. 1 µl of each solution was mixed with 1 ng of a 5 x 10 4 cpm 304 nt RNA probe and incubated at 37°C for one hour. 5 µl .
Figure 2. Effects of DEPC Treatment of Various Buffers. One µg/ml RNase A was added to various buffers along with 0.1% or 1% DEPC. Solutions were vigorously shaken for 1 minute, incubated for 1 hour at room temperature and autoclaved for 25 minutes. 1 µl of each solution was mixed with 1 ng of a 5 x 10 4 cpm 304 nt RNA probe and incubated at 37°C for one hour. 5 µl .
is the ppr test hard
rnase inhibitor removal
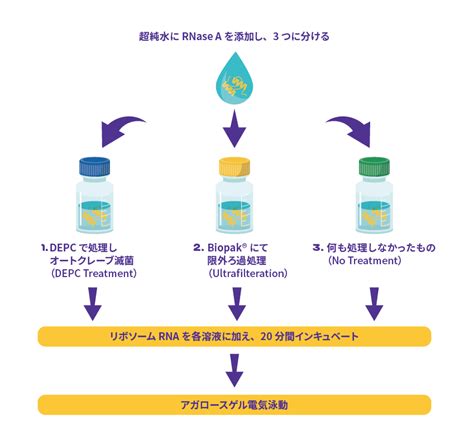
RNase removal methods include RNase inhibition and RNase decontamination. NOTE: It is highly recommended that a dedicated space be set aside for procedures that require RNase treatment to avoid inadvertent exposure of RNA samples to RNase.The water delivered is RNase-free and does not require DEPC treatment or autoclaving. Figure 2. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) photo showing a cross-section of one of the ultrafiltration polysulfone hollow fibers contained in a Biopak ® polisher.
DEPC treatment of solutions is accomplished by adding 1 milliliter DEPC per liter of solution, stirring for 1 hour, and autoclaving for 1 hour to remove any remaining DEPC. However, DEPC may not always be appropriate, as it can react with .Merely autoclaving will not destroy all RNase activity, since these enzymes are very robust and can regain partial activity upon cooling to room temperature. . RNAsecure, is also available that can be used to treat primary amine solutions such as TRIS and does not require a 2 hr treatment nor autoclaving. Laboratory Surfaces . Contact with .These RNases are resistant to metal chelating agents and some of them, like RNase A family enzymes, can survive prolonged boiling or autoclaving. RNase A-type enzymes rely on active site histidine residues for catalytic activity (1) and can be inactivated by the histidine-specific alkylating agent diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC).
RNase inhibitors are recombinant enzymes that inhibit the activity of RNases. Since RNases are ubiquitous in the laboratory environment—on your skin, in the air, on anything touched by bare hands, or on anything left open to the air—it is important to make an effort to prevent or eliminate RNase contamination, which can be done with the use of RNase inhibitors.
portion of the RNase is inactivated by autoclaving, otherwise the RNA probe would remain intact at any RNase concentration. Autoclaving alone may be sufficient to eliminate enough RNase for some .Figure 2. Effects of DEPC Treatment of Various Buffers. One µg/ml RNase A was added to various buffers along with 0.1% or 1% DEPC. Solutions were vigorously shaken for 1 minute, incubated for 1 hour at room temperature and autoclaved for 25 minutes. 1 µl of each solution was mixed with 1 ng of a 5 x 10 4 cpm 304 nt RNA probe and incubated at 37°C for one hour. 5 µl .No, autoclaving is not sufficient to remove RNases. Typically you either have to treat everything with DPC and bake glassware at above 180 C overnight in order to get rid of RNases. And for tips, it's easiest to just buy RNase/DNase free tips as standard ones can melt at those temperatures.
Figure 2. Effects of DEPC Treatment of Various Buffers. One µg/ml RNase A was added to various buffers along with 0.1% or 1% DEPC. Solutions were vigorously shaken for 1 minute, incubated for 1 hour at room temperature and autoclaved for 25 minutes. 1 µl of each solution was mixed with 1 ng of a 5 x 10 4 cpm 304 nt RNA probe and incubated at 37°C for one hour. 5 µl .Protocol 1. Preparation of RNase-free solutions 1. Add 0.1 ml DEPC to 100 ml of the solution to be treated. Shake vigorously to bring the DEPC into solution. 2. Incubate for 12 h at 37°C. 3. Autoclave for 15 min to remove any trace of DEPC. DEPC will react with primary amines and cannot be used directly to treat Tris buffers. DEPC is highly
Use 0.5 mL DEPC/L, incubate for 2 hr, autoclave for 45 minutes minimum. DMPC can also be used and may be be safer than DEPC, which is a known carcinogen. Alternatively, many vendors offer certified nuclease-free water, which may be worth the investment. Note that ultrafiltered water is already RNase free so does not need DEPC treatment.
Protocols state very different autoclave times. If the fruity smell is faint, autoclaving was sufficient. Even after a long 45min autoclave treatment the smell will not be completely gone. If you use more than 0.05% and have a very sensitive downstream experiment, it does not hurt to autoclave longer or twice. WarningsDEPC treatment, Invitrogen™ RNAsecure™ reagent, is also available and can be used to treat primary amine solutions such as Tris and does not require a 2-hour treatment or autoclaving. DEPC treatment is the most commonly used method for eliminating RNase contamination from water, buffers, and other solutions.
rnase and depc treatment
DEPC treatment, Invitrogen™ RNAsecure™ reagent, is also available and can be used to treat primary amine solutions such as Tris and does not require a 2-hour treatment or autoclaving. DEPC treatment is the most commonly used method for eliminating RNase contamination from water, buffers, and other solutions.
is the practice teas test harder
Add 1 part 99% glycerol in a sterile bottle. Add 1 part of sterile H2O and mix until the glycerol is completely dissolved. Autoclave the solution.
does autoclaving treat rnase|can rnase be inactivated